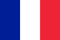
Osteoarthritis is a pathology in which there is a gradual deformation of the joints. In the early stages, the cartilage and ligaments are destroyed. The process proceeds slowly, so the disease is detected already at an advanced stage of development. In the future, this can lead to the loss of mobility and disability.
The risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with age. The disease affects men and women equally.
Symptoms
Joint pain when moving is the main symptom of the disease, as a result of which many seek medical help on time. Discomfort occurs during a long walk or strong physical exertion.
What is osteoarthritis, the doctor will tell when diagnosing the disease. Pathology can be suspected when the following symptoms appear:
- night pains resulting from stagnation of venous blood and increased pressure within the joint;
- the appearance of a creak due to the friction of the collapsed cartilage;
- increased pain during heavy loads, this is especially expressed in knee arthrosis during squats, sports (running, jumping, weight lifting), carrying weights;
- weather dependence, when the affected joints begin to hurt when the weather changes, especially before rain or heavy snow, cold stroke;
- morning stiffness.
The difference between osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis, the doctor's response
A medical doctor and popular health television host says the terms "osteoarthritis" and "osteoarthritis" mean a disease in which cartilage is damaged and bone grows.
With arthrosis, the cartilage tissue of the surface of the joints is destroyed, the mobility of the limb is limited, severe pain appears. Pathology is diagnosed in men and women over the age of 40 (the main reason in women is the onset of menopause, when hormonal changes occur in the body).
Osteoarthritis occurs as a result of the deformation of the articular cartilage and affects the bone tissue, affecting the entire joint, leading to disability.
Other diseases with similar symptoms
There are a number of diseases that have similar signs to those of osteoarthritis:
- Humeroscapular periarthritis, cervical osteochondrosis, osteoporosis and arthritis of the shoulder joint.
- Epicondylitis of the elbow, deforming osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis of the hand.
- Coxarthrosis.
- Rheumatoid and infectious arthritis in children.
Types of osteoarthritis by localization
Varieties of the disease vary depending on where the diseased joint is located. The mildest type of pathology is the shoulder. Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed:
- cervical region;
- knee joint (affects both legs, but develops to varying degrees);
- ankle;
- hip joint (a condition characteristic of the elderly).
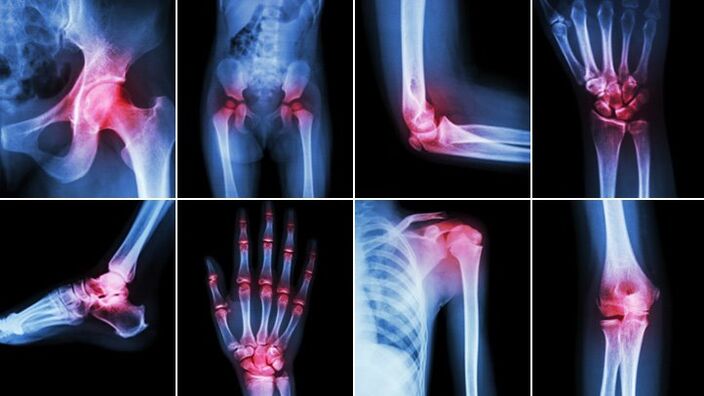
Causes of the disease
The disease can develop without cause (idiopathic or primary). Pathological processes in the body often provoke a secondary form of pathology. Reasons for the development of arthrosis:
- injuries (dislocations, bruises, fractures, ligament tears, damage to the meniscus);
- congenital anomalies in the development of the joints (dysplasia);
- metabolic disease;
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- inflammatory processes (acute purulent arthritis);
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, encephalitis, gonorrhea, syphilis);
- pathology of the endocrine system (thyroid disease);
- haemophilia;
- age-related changes in the body;
- frequent hypothermia.
Diagnostics
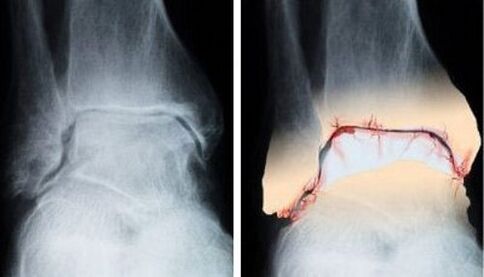
There are several diagnostic methods:
- radiographic examination;
- arthroscopy (examination with a video camera inserted into the joint through a 4-5 mm incision);
- blood analysis;
- histological examination of the synovium (with arthrosis, integumentary cells do not regenerate, atrophic villi appear, the number of vessels decreases).
The degree of damage to the joint
One classification is used, including 4 degrees of disease development.
The first stage (the disease does not affect the ability to work):
- slight limitation of joint movement in one direction only;
- there are no bone growths on the x-ray;
- the surfaces of the cartilage are uneven;
- the narrowing of the joint space begins.
The second phase (affects the ability to work):
- average movement limitation;
- loud crunching when changing the position of the limb;
- partial atrophy of neighboring muscles;
- bone growths, osteophytes;
- the lumen of the gap is 2-3 times less than the norm.
Third stage (disability):
- joint deformity;
- movement is limited;
- pain during movement and at rest (relieved by painkillers);
- there is no joint space;
- the muscles are atrophied;
- ossification of the articular surface.
Fourth stage:
- severe pain that does not go away after taking painkillers.
- complete destruction of the joint.
Basic treatments
Osteoarthritis therapy includes several methods. To get a positive result, you need to take medications, monitor weight. Physiotherapy, kinesitherapy are prescribed. In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed.
doctor
The main task in the treatment of arthrosis is the removal of pain. For this, drugs of different groups are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal drugs in the form of tablets, suppositories, ointments, gels, injections. Long-term use of these drugs adversely affects cartilage tissue.
- Corticosteroids. They are used in severe cases to relieve pain, do not slow down the development of the disease. With uncontrolled use, the cartilage thins.
- Analgesics, antispasmodics. Poorly relieves inflammation, but effective in relieving pain.
- Chondroprotectors. These are the main drugs for the treatment of arthrosis, provide nutrients to cartilage tissues, stimulate cell regeneration. They do not have a quick effect, the condition of the joints gradually improves. Also effective at stage 3 of the disease.
- Vasodilator drugs. Necessary to improve blood circulation, eliminate spasms of small vessels. Enhances the action of chondroprotectors.
Physiotherapy
With osteoarthritis, physiotherapy is used effectively. Procedures include warming up the joints. Dry heat slows down the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue, reduces pain and improves the general condition of the patient.
The following methods are used to treat the disease:
- ultrasonic impact. High-frequency sound acts on the body's tissues, causing a number of beneficial effects. With the micromassage, the muscles are warmed up, the blood flow in the capillaries improves and the metabolic processes are accelerated.
- Electrophoresis. Under the influence of a low-voltage current, drugs are injected into the problem area without affecting other parts of the body.
- magnetotherapy. Applying the method helps reduce inflammatory reactions, strengthens blood vessels, improves blood flow and accelerates cell regeneration in the problem area.
- Radiation exposure (use of infrared, ultraviolet or laser rays). It is used in addition to other methods of physiotherapy or in case of contraindications to their use.
Surgical
In the absence of positive dynamics in the treatment of arthrosis, surgical methods are used:
- Operational interventions. There are 4 types: joint-preservation, joint-replacement, joint-resection, joint-strengthening. The choice depends on the degree of development of the disease, the intensity of pain, the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Sting. It is performed with progressive osteoarthritis. It performs 2 functions: relieves pain in the damaged joint and relieves tension inside the capsule, removing from it substances that destroy cartilage tissue. It is an informative diagnostic method. During this procedure, after local anesthesia, drugs are injected into the joint.
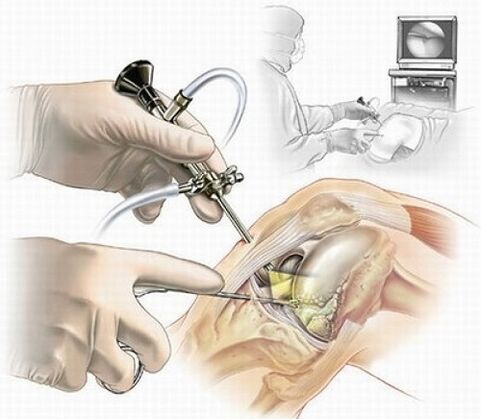
- Arthroscopy. Often performed on an outpatient basis. During the procedure it is possible to remove sections of cartilage or bone from the joint, treat the meniscus, rebuild the ligament apparatus and clean the joint surfaces deformed during osteoarthritis. It is performed under general or local anesthesia.
- Arthrotomy. The opening of the joint is done if the arthroscopy did not give a positive result. It is indicated for prolonged joint swelling and constant intense pain that is not stopped by drugs. It is recommended if you want to remove large fragments of cartilage or bone tissue.
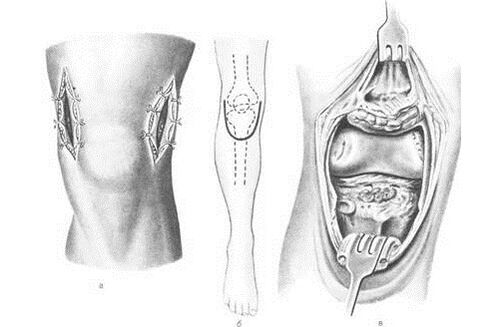
Operations to change the position of the joint are performed in cases where it is necessary to correct the position of the bones, with defects in the structure of the joints, as a prevention of arthrosis.
physical therapy
Physiotherapy exercises can help in the early stages of the disease, when the joint is not yet deformed. Active movements slow down the course of the disease, but with joint damage, when the disease has passed into later stages, physical exercises can contribute to the development of exacerbation and destruction of tissues in the problem area.
You need to do this only after consulting a specialist who will help you choose a set of exercises and master the implementation methodology. The first training should take place under the supervision of an instructor.
When performing exercises, you need to follow the rules:
- Avoid stress on the injured joint.
- A moderate pace of exercise does not cause joint destruction.
- Rest and exercise must be balanced.
- Strong loads and high intensity of movement cause increased pain and cause swelling of the joint.
- In any position of the body it is necessary to remember the correct posture.
Regular physical therapy exercises help increase range of motion, relax muscles, and improve the patient's overall condition.
Manual therapy
In combination with drugs in the treatment of arthrosis, manual therapy methods are used that increase the mobility of damaged joints, prevent muscle atrophy and positively affect the patient's entire body.
During the session, the following manipulations are performed:
- Relaxation (complete relaxation) of the muscles involved in the work of the diseased joint.
- Perform low-frequency mobilization of the joint surface to expand the range of motion of the joint to the limit of its mobility.
- Acupressure according to the Schwartz method to bring the muscles to a state of rest.
- The use of laser therapy and the apparatus.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies are actively used in the treatment of arthrosis to activate the production of collagen, the basis of tendons and cartilage. They also relieve joint swelling and reduce pain. Recipes include plants such as thyme, cinquefoil, dandelion (root), strawberry and birch leaves, and willow bark.

There is a simple but effective way to use birch leaves. To do this, you need to choose comfortable clothes that fit perfectly in the area affected by osteoarthritis (high stockings or socks suitable for the ankle, tight stockings for knee treatment and sealed leggings for the hip joint). At night, it is necessary to cover the diseased joint with leaves and wear suitable clothes. You cannot wrap the fabric with polyethylene.
The leaves extract salts, toxins and cholesterol deposits from the diseased joint, the skin after the procedure becomes smooth and velvety. The course of treatment is 6-7 procedures, before use, a doctor's consultation is required, because. there may be contraindications for use.
In folk medicine, ointments, infusions, freshly squeezed juices, compresses are used to combat osteoarthritis, which are often recommended by doctors in combination with drugs. The action of all non-traditional remedies is aimed at reducing pain and swelling of damaged joints, repairing tissues and improving the general condition of the patient.
But you can not engage in self-medication, otherwise complications may arise.
It is necessary to revise the diet
With osteoarthritis it is necessary to adjust nutrition, which should aim at improving metabolic processes, reducing body weight if necessary, strengthening connective and cartilaginous tissues and ligaments. There is no special diet. To achieve good results in treatment, the following rules must be observed:
- Take into account the calorie content of meals so that in patients with normal weight it remains stable and in overweight patients returns to normal.
- Fatty, smoked, semi-finished dishes containing flavor enhancers, dyes and preservatives are prohibited.
- Products should be natural: low-fat varieties of fish and meat, seafood rich in minerals and vitamins, fresh fruits and vegetables, hard cheese, butter, low-fat cottage cheese, nuts, chicken eggs, bread of rye and bran, high quality vegetable oil rich in unsaturated fatty acids.
- It is necessary to limit the daily intake of salt to 8 g.
- Drink at least 2-2. 5 liters of water per day.
- Include in the diet foods that include natural chondroprotectors: lean chicken, cartilage, red fish, hard cheese. Increase the use of gelatin, which normalizes the structure of cartilage tissue, strengthening it. To do this, it is necessary to include in the menu various jellies, jellies, aspic fish, kisses.
- It is necessary to spend 2-3 days of unloading a week (cottage cheese, kefir, fruit and vegetable day).
What are the dangers of the different stages of the disease
In the initial stage of the disease, osteoarthritis manifests itself with periodic pain in the joints and partial limitation of mobility. The danger of the disease is that if you ignore its first symptoms, in the later stages of development, the pathology will lead to the destruction of joint tissues. Consequences: complete loss of mobility. The patient is assigned a disability group depending on the degree of development of the disease and the condition of the joints.
Prevention
Prevention of osteoarthritis is as follows:
- Body weight control.
- Proper balanced nutrition.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Avoid hypothermia of the joints.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- A healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
The danger of the disease is that a person can completely lose mobility. Knowing the symptoms of the disease, the causes of its development and methods of struggle, you can get rid of the pathology in the early stages.